Geometric and information modelling of museums and collections: the Invisible Archaeology temporary exhibition at the Museo Egizio in Turin
ABSTRACT
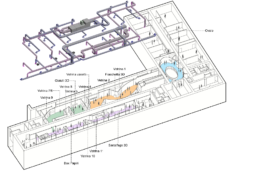
The essay critically evaluates the application fields of BIM and VPL processes used in the management and valorisation of museum heritage, pursuing parametric and algorithmic approaches, successfully employed in the digitisation project of the temporary exhibition Invisible Archaeology set up in the exhibition spaces of the Museo Egizio of Turin.
Elisabetta Caterina Giovannini, Massimiliano Lo Turco, Andrea Tomalini
Politecnico di Torino, Dipartimento di Architettura e Design
BIM for the management of the intervention on monumental architecture: the case study of former nineteenth century prison in Parma
ABSTRACT
The paper explains the peculiarities of the BIM model of the former prison of San Francesco del Prato in Parma, case study analyzed in the context of the project “POR-FESR 2014-2020 Existing Building Information Modelling for the management of the intervention on the existing building”.
Chiara Vernizzi, Roberto Mazzi
Università di Parma, Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Architettura e CIDEA, Centro Interdipartimentale per l’Energia e l’Ambiente
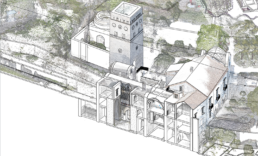
Image-based elaborations to improve the HBIM level of development
ABSTRACT
A Scan-to-BIM approach, starting from a 3D UAV survey, led to a HBIM parametric modeling and final texturing employing photogrammetric imagery. The purpose is to keep access to the information of the smart objects, for cultural heritage dissemination and conservation purposes and for a real-time photorealistic visualization.
Carla Ferreyra, Anna Sanseverino, Andrea di Filippo
Dipartimento di ingegneria civile, Università degli Studi di Salerno
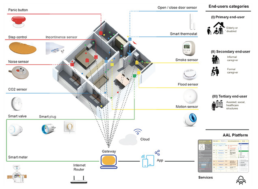
BIM and IoT for Healthcare: digital models and services for care and assistance
ABSTRACT
The contribution illustrates the development of a digital model of an Ambient Assisted Living (AAL) space for frail end-users, for the control and the management of information flows referred to a range of IoT devices and of an ICT platform for care and assistance services. The logic of relational databases has been used as an expedient for tracking heterogeneous data, providing for the replicability and the extension of the BIM model to multiple contexts of use.
Anna Mangiatordi
Sapienza Università di Roma, Dipartimento DIAP
Reviewer 2021
REVIEWER 2021
Pietro Baratono, Provveditore Interregionale per le OO.PP. Lombardia ed E.Romagna
Angelo Ciribini, Presidente ISTEA, Università di Brescia, Brescia, Italy
Bruno Daniotti, Project Manager InnovAnce, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy
Alberto Pavan, Coordinatore norma UNI 11337, Responsabile Scientifico InnovAnce, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy
Gregorio Cangialosi, BIM Manager and BIM Strategist, Studio CABE, Torino, Italy
Emmanuel di Giacomo, EMEA BIM & AEC Ecosystem Business, France
Graziano Lento, Anafyo Sagl, Ticino, Switzerland
Paolo Galli, Implementation Consultant BIM, Milano, Italy
Diego Minato, BIM Manager & Technical Consultant | BIM Strategist, Treviso, Italy
Orges Lesha, BIM Manager, SA Architects, Sdn Bhd, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Chiara Rizzarda, Deputy BIM Manager at Antonio Citterio Patricia Viel, Milano, Italy
Yoseph Bausola Pagliero, VPL and BIM expert, Roma/ Torino, Italy
Armando Casella, Bimfactory, Brescia, Italy
Filippo Daniele, Setin Roma, Italy
Yusuf Arayici, Hasan Kalyoncu University, Gaziantep, Turkey
Maarten Bassier, University of Leuven, Leuven, Belgium
Stefano Bertocci, Università degli Studi di Firenze, Firenze, Italy
Carlo Bianchini, Sapienza Università di Roma, Roma, Italy
Maurizio Bocconcino, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy
Frédéric Bosché, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Stefano Brusaporci, Università degli Studi dell’Aquila, L’Aquila, Italy
Clark Cory, Purdue University, Indianapolis, USA
Livio De Luca, MAP/CNRS, Marseilles, France
Antonella Di Luggo, Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II, Napoli, Italy
Stephen Fai, Carleton University, Ottawa, Canada
Pablo Lorenzo Eiroa, Cooper Union, New York, USA
Andrea Giordano, Università degli Studi di Padova, Padova, Italy
Antonio Gómez-Blanco Pontes, Universidad de Granada, Granada, Spain
Sorin Hermon, Cyprus Institute, Nicosia, Cyprus
Arto Kiviniemi, University of Liverpool , Liverpool, United Kingdom
Giovanna Massari, Università degli Studi di Trento, Trento, Italy
Maurice Murphy, Dublin Institute of Technology, Dublin, Ireland
Anna Osello, Politecnico di Torino, Torino, Italy
Livio Sacchi, Università degli Studi “G. d’Annunzio”, Chieti-Pescara, Italy
Andrew Sanders, Penn University, Philadelphia, USA
Alberto Sdegno, Università degli Studi di Trieste, Trieste, Italy
Jose Pedro Sousa, Universidade do Porto, Porto, Portugal
Massimo Stefani, Harpaceas
Anna Dell’Amico, Università degli Studi di Pavia, Pavia, Italy
Francesco Livio Rossini, Sapienza Università di Roma, Roma, Italy
Index Volume 7
INDEX
Editorial
Sandro Parrinello, Massimiliano Lo Turco
From Building to Media: Envisioning Information in OMA
Fabio Colonnese
Accessible informations. Visualizing data in the age of big data, open data and open tools
Enrico Cicalò, Valeria Menchetelli
From type to diagram: data representation as heuristic tool for architectural design
Michela Barosio, Rossella Gugliotta
Graphic visualization and new ways to represent data
Maurizio Marco Bocconcino, Mariapaola Vozzola
H-BIM: information flows and data digitization processes
Anna Dell’Amico
Knowledge representation through cognitive maps to foster collaborative research
Elena Gigliarelli, Filippo Calcerano, Michele Calvano, Stefano Cursi, Leo Lorenzi, Letizia Martinelli, Maurizio Sibilla
From OpenData to city models: an Anti-Fragile approach for City Information Modeling
Federico Mario La Russa, Cettina Santagati
Reflections on the use of HBIM from experiments on the field
Carlo Battini, Rita Vecchiattini
Documentation of frescoed surfaces in HBIM models
Simona Scandurra
Graphical communication of the ‘Torre dei Grassi’ at the ‘Portico d’Ottavia’ in Rome
Giulia Pettoello
An algorithmic information model (AIM) for the map of decay: the Church of San Giuliano
Elisabetta Caterina Giovannini, Andrea Tomalini
Editorial Vol. 07
“Graphic excellence is nearly always multivariate”
(Edward Tufte, The Visual Display of Quantitative Information, 1983)
The journal’’s seventh issue collects a selection of the contributions received in response to the call entitled “The wide possibilities of data representation.”
The result was a very diverse collection of research and experiences, albeit related to two interesting macro-themes referable to the multiple forms of graphic processing: the infographics of digital models and the development of information models. Some essays describe in detail the expressive potential of new infographic representation tools useful for a synthetic representation, also of a statistical type, to govern new knowledge processes.
An increasingly professional and specialized knowledge described in many contributions that question the resolution of increasingly complex challenges, in the organization of attributes of a heterogeneous type and not only quantitative in nature, broadening the frontiers of the Drawing discipline, as also testified by the success of an important interdisciplinary event on the theme of “graphics” held in Alghero in July 2019, concerning the different meanings of what pertains to the sphere of -graphics, as in description, study, writing, drawing. An open, interdisciplinary knowledge, as evidenced by the various figures who contributed to the achievement of the journal’s new issue.
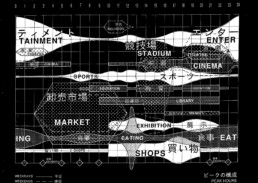
Some contributions refer more precisely to this first issue, relating to methods and examples of data representation: the essay by Fabio Colonnese critically analyzes the role of architectural design in communications by the architecture firm OMA, to indicate a gradual migration towards the use of quantitative schematic diagrams and visual representations produced by a systematic crossing of statistical data, simplified plans and volumetric diagrams integrated by texts, symbols, and patterns, to illustrate and explain the process and the shape of the project and the functional solutions.
Moreover, concerning the representation of the architectural project, the contribution of Michela Barosio and Rossella Gugliotta is aimed at investigating the relationship between type and diagram, often considered as mere simplifications of reality by analyzing how the diagram is increasingly placed with greater force as a tool for conception and explanation of the design process.
Elena Gigliarelli’s working group’s reflections appear to be of an interdisciplinary nature. There is evidence of the need for a synergy between different fields of knowledge underlying the use of a knowledge-sharing language through cognitive maps and graphic codes for the synthesis of concepts.
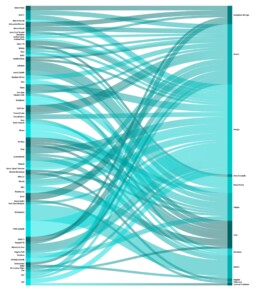
The contributions of Enrico Cicalò with Valeria Menchetelli and Maurizio Marco Bocconcino with Mariapaola Vozzola present a more theoretical approach. The first critically analyzes the potential of Data Visualization in the era of Big Data, highlighting how the excellent availability of open data and open tools reinforces the need for a designer-based scientific approach; the second reflects on the classification of data processing methods that helps to select the most effective representation methods by verifying the applications, including the scientific ones, which make it possible to obtain different visualization types. This analysis is critically conducted by commenting on examples of graphic representation that give “information” starting from “data”.
The contributions that deal more specifically with the development of information models focus on data visualization as a tool for the representation of complex data systems, joined with Data Collection activities, illustrated through original and innovative approaches.
In Giulia Pettoello’s contribution, the different ways an architectural asset can be documented and communicated are investigated. Anna Dell’Amico proposes the use of standard protocols for the management of shared models by employing a common language that facilitates the exchange of information. Although referring to the urban scale, the research by Cettina Santagati and Federico Mario La Russa investigates responsive models that increase the quantity and quality of data related to City Information Modeling models.
The other essays provide an opportunity to reflect on the role of the BIM Heritage by understanding and analyzing them, including the difficulties, limits, and the potential that the system can offer in the field of conservation and documentation.
In particular, Carlo Battini and Rita Vecchiatini critically reflect on the possibility of collecting heterogeneous information such as metric surveys and three-dimensional models, documentary, cartographic and iconographic sources, textual information, of both a punctual and spatial nature, which can be aggregated into a single database, for the planning of conservation interventions and the related cost calculation, without neglecting the possibility of extracting data useful for routine maintenance and in general for the building management.
Simona Scandurra’s essay intends to examine a possible approach to the documentation of architectural heritage in the context of HBIM, with particular reference to the storage and management of data relating to wall decorations characterizing the wall surfaces of some historical artifacts.
In the end, the contribution of Elisabetta Caterina Giovannini and Andrea Tomalini reflects on the union between three-dimensional modeling and information modeling, through workflows that include programming approaches with nodal systems and machine learning algorithms for the generation of new components: starting from data acquisition of a survey and the subsequent data processing, innovative solutions for the classification and semiautomatic creation of degraded elements are proposed. Therefore heterogeneous contributions in their applicative experiences, albeit attributable to similar purposes, aimed at identifying models of representation of information useful for carrying out comparative readings. By developing digital models and data management structures, representation intends to favor more intuitive interpretations to exponentially expand the possibilities of relating complex data sets. The chance of associating heterogeneous data and developing comparisons will result in cultural enrichment, not only in technical and operational skills.
The drawing representation expresses the human value of the sign’s interpretation; therefore, qualifying models and information systems through signs and symbols implies humanizing an information system to benefit a more natural and sensitive relationship with new digital complexity.
Sandro Parrinello, Massimiliano Lo Turco
From Building to Media: Envisioning Information in OMA
ABSTRACT
The role of architectural drawing in OMA’s communication has been gradually readdressed and eclipsed by diagram, quantitative schematic visual representation resulting from a systematic crossbreeding between statistical analysis, simplified plans and volumetric schemes with texts, symbols and patterns, in order to envision and clarify program, design process and form, and functional solutions.
Fabio Colonnese
Sapienza Università di Roma
Accessible informations. Visualizing data in the age of big data, open data and open tools
ABSTRACT
This article discusses the potential of data visualization in the era of Big Data, highlighting how the great availability of open data and open tools strengthen the need for a designer-based scientific approach capable of going beyond the current affirmation of user-generated content (UGC).
1) Enrico Cicalò, 2) Valeria Menchetelli
1) Università di Sassari, 2) Università di Perugia
From type to diagram: data representation as heuristic tool for architectural design
ABSTRACT
In the field of architectural design, representation is a growingly fundamental tool for the conception process. The paper attempts to enquire about the relationship between type and diagram, both often regarded as mere simplifications of reality, starting from the observation that diagram is increasingly considered as a tool able to explicit the conception process in architecture.
Michela Barosio, Rossella Gugliotta
Politecnico di Torino I DAD