HBIM for public administration management. The case study of Palazzo Vitelli alla Cannoniera.
ABSTRACT
This paper reports the first results concerning the experimentation of information management of HBIM artefacts owned by municipalities, as a result of a research path aimed at determining methodologies and protocols for the representation of these classes of assets, with the aim of simulating future interactions with designers in correspondence with future public tenders.
F. Bianconi, M. Filippucci, A. Parisi, S. Battaglini
University of Perugia
Scan-to-HBIM: integrated survey and information modelling for the documentation of structural damage
ABSTRACT
The research presents an experimental approach for the damage documentation of existing structures. The main aim is to identify a methodology from the integrated digital survey (range- and image-base) to BIM to synthesise quantitative information on the existing damage that can be exported for the structural assessments.
Simone Balin, Giuliana Cardani, Fausta Fiorillo
Politecnico di Milano
Index Volume 8
INDEX
Editorial
Cecilia Bolognesi, Cettina Santagati
Knowing the built heritage through digitised procedures. The index of masonry quality integrated in HBIM processes
Filippo Calcerano, Letizia Martinelli, Michele Calvano, Elena Gigliarelli
Heritage BIM for the survey, representation and restoration of existing heritage, a case of study: the Marciana fortress on Elba island
Sara D’Ippolito, Laura Gianzi, Marzia Monaco
Mixed Reality experiences for the heritage of Francesco di Giorgio Martini:reconstruction of the Cagli’s fortress
Paolo Clini, Ramona Quattrini, Romina Nespeca, Mirco D’Alessio
Digital meets Opera: an interactive service model towards accessibility and sustainability.
Daniela De Luca, Francesca Maria Ugliotti
BIM-based Data Management in Built Heritage Life Cycle: a comparison of methods
Andrea Bongini, Vincenzo Donato, Carlo Biagini
City Information Modeling and seismic risk: integrated HBIM-GIS approaches for the management of post-earthquake scenarios
Federico Mario La Russa, Giulia Genovese
Geometric and information modelling of museums and collections: the Invisible Archaeology temporary exhibition at the Museo Egizio in Turin
Elisabetta Caterina Giovannini, Massimiliano Lo Turco, Andrea Tomalini
BIM for the management of the intervention on monumental architecture: the case study of former nineteenth century prison in Parma
Chiara Vernizzi, Roberto Mazzi
Image-based elaborations to improve the HBIM level of development
Carla Ferreyra, Anna Sanseverino, Andrea di Filippo
BIM and IoT for Healthcare: digital models and services for care and assistance
Anna Mangiatordi
Editorial Vol. 08
New parametric objects
This number of Dienne has chosen the Digital Twin as the subject of its discussion, a development area that is intertwined with that of BIM, representing a first important evolution in terms of applications.
It is therefore very easy to find in the path leading to the completion of this more general theme, attempts to make the structure of the basic model dialogue with different data, which in fact oblige the implementation of increasingly advanced methods and tools to interface with complex relationships. .
These are the contents of this issue of Dienne; an issue that collects the best papers selected from those presented as part of the 3D Modeling and BIM conference held online on April 14, 2021, organized by Sapienza University of Rome where the in-depth study of HBIM applications crosses areas ranging from parameterization of degradation, to the creation of specific parametric objects, to the use of advanced methodologies through the VPL, to augmented reality applications for management.
The peculiarities of the BIM approach aimed at the recovery intervention on built heritage are highlighted in the contribution of Sara D’Ippolito, Laura Gianzi and Marzia Monaco which illustrates the experiments on the informative reliability of the model starting from historical surveys, information found on the web and digital surveys. In the same direction, the contribution of Chiara Vernizzi and Roberto Mazzi on the former prison of San Francesco del Prato in Parma which shows the maturity in the adoption of BIM processes for existing assets.
A critical evaluation of the BIM approach in the management and enhancement of museum heritage emerges in the contribution of Elisabetta Caterina Giovannini, Massimiliano Lo Turco and Andrea Tomalini who experiment with parametric and algorithmic approaches on the Egyptian Museum; the theme of the dissemination and conservation of cultural heritage, for a real-time visualization starting from an H-BIM model obtained from integrated digital survey techniques, is central in the contribution of Carla Ferreyra, Anna Sanseverino and Andrea di Filippo; on the other hand, the reflection conducted by Paolo Clini, Ramona Quattrini, Romina Nespeca and Mirco D’Alessio on the methods of narrating material and immaterial heritage leads to the innovative experimentation of mixed-reality techniques at the Rocca Torrione complex by Francesco Di Giorgio Martini.
Daniela De Luca and Francesca Maria Ugliotti experiment with the Digital Twin paradigm on Teatro Regio in Turin, configuring a dynamic and interactive model of the building that provides for a constant interaction between real and virtual space.
The working group made up of Andrea Bongini, Vincenzo Donato and Carlo Biagini faces the potential and current limits of some BIM-based approaches in the field of Facility Management by comparing two different processes for the acquisition and management of the parameters necessary for the phases of asset management of existing school buildings
In the context of historical heritage, both at the architectural and urban scale, the issues relating to the assessment of seismic vulnerability and post-earthquake management are of great interest, which require the collection and systemization of heterogeneous data, also through Visual Programming Languages, for the creation and implementation of H-BIM workflows as in the case of the contribution of Filippo Calcerano, Letizia Martinelli, Michele Calvano and Elena Gigliarelli or of an approach to the urban scale as reported in the contribution of Federico Mario La Russa and Giulia Genovese for the creation of a responsive City Information Modeling.
Finally, the contribution by Anna Mangiatordi illustrates the development of a digital model of assisted living for the elderly for the control and management of information flows related to the insertion of Artificial Intelligence systems into the environment, through a BIM data sharing platform based on on open and interoperable information processes.
In the continuation of the next issues, the ongoing evolutionary process that pushes BIM beyond its first vocations will certainly be able to carry on all the research areas undertaken up to now and show us how fertile and interesting developments are here.
Cecilia Bolognesi, Cettina Santagati
Knowing the built heritage through digitised procedures. The index of masonry quality integrated in HBIM processes
ABSTRACT
The research aims to integrate the Index of Masonry Quality into a Heritage BIM workflow, with the support of Visual Programming Language (VPL). The study is part of a broader set of investigation methods for the digitisation of built heritage for facilitating the management and accessibility of information. By reducing analyses’ costs and time, it is suitable for urban scale evaluation of vernacular historic centres.
Filippo Calcerano, Letizia Martinelli, Michele Calvano, Elena Gigliarelli
ISPC Institute of Heritage Science, National Research Council of Italy
Heritage BIM for the survey, representation and restoration of existing heritage, a case of study: the Marciana fortress on Elba island
ABSTRACT
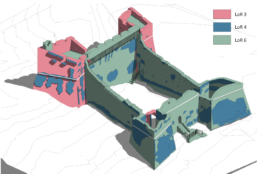
The HBIM methodology applied to a historical asset is an extremely interesting topic for the study of Italian heritage. In order to reach a good level of information about the fortress, several steps have been performed using IT and web tools. Thanks to the historiographical analysis we have been able to hypothesize a probable date of origin, while surveys with laser scanners, drones and photography – for the identification of decay form – were indispensable for architectural modeling. Appreciable results were obtained both with the representation of the model and with its informative reliability, implementing the digital twin through the design of recovery interventions and the management of times and costs.
Sara D’Ippolito, Laura Gianzi, Marzia Monaco
Mixed Reality experiences for the heritage of Francesco di Giorgio Martini: reconstruction of the Cagli’s fortress
ABSTRACT
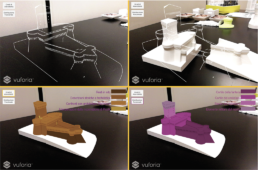
The present work constitutes a significant and innovative step in the testing of solutions for the interaction with digital facsimiles, in particular it investigates the potential of Mixed reality applications for the communication of three-dimensional modelling projects. In this case, the 3D reconstruction of the Rocca-Torrione complex by F. di Giorgio Martini in Cagli is the exemplar case study on which is possible to test the principles of the reference charts in the field of Digital Cultural Heritage (DCH) but also to reflect on methodologies of storytelling for the tangible and intangible heritage. Furthermore, these studies, together with the local and regional networks, represent the precondition for the creation of a Study Centre on Francesco di Giorgio Martini which will be based in Cagli.
Paolo Clini, Ramona Quattrini, Romina Nespeca, Mirco D’Alessio
Università Politecnica delle Marche
Digital meets Opera: an interactive service model towards accessibility and sustainability.
ABSTRACT
This paper presents the results of a research aimed at demonstrating the potentialities and cur-rent limits of some BIM-based approaches in the field of Facility Management. Today the man-agement and interpretation of large amounts of data of different nature and disciplinary scope is one of the most relevant problems in the definition of new and more efficient information manage-ment processes in the construction sector.
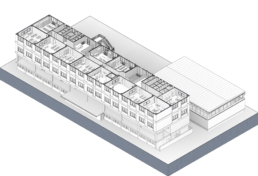
Two different processes are compared for the acquisition and management of the parameters needed for the asset management phases of existing school buildings. The first method involves the compilation of schedules within the BIM authoring software by means of an appropriate mapping of the parameters with reference to the information exchange scheme established by COBie (Construction-Operations Building Information exchange); the second method uses a spe-cific software for FM, dRofus, which is able to create a direct link with the BIM authoring software for the bi-lateral writing of the parameters. Through a comparative analysis, the results of the case study G. Rodari Primary and Infant School in Florence are discussed.
Daniela De Luca, Francesca Maria Ugliotti
Politecnico di Torino
BIM-based Data Management in Built Heritage Life Cycle: a comparison of methods
ABSTRACT
This paper presents the results of a research aimed at demonstrating the potentialities and cur-rent limits of some BIM-based approaches in the field of Facility Management. Today the man-agement and interpretation of large amounts of data of different nature and disciplinary scope is one of the most relevant problems in the definition of new and more efficient information manage-ment processes in the construction sector.
Two different processes are compared for the acquisition and management of the parameters needed for the asset management phases of existing school buildings. The first method involves the compilation of schedules within the BIM authoring software by means of an appropriate mapping of the parameters with reference to the information exchange scheme established by COBie (Construction-Operations Building Information exchange); the second method uses a spe-cific software for FM, dRofus, which is able to create a direct link with the BIM authoring software for the bi-lateral writing of the parameters. Through a comparative analysis, the results of the case study G. Rodari Primary and Infant School in Florence are discussed.
Andrea Bongini, Vincenzo Donato, Carlo Biagini
University of Florence, DIDA
City Information Modeling and seismic risk: integrated HBIM-GIS approaches for the management of post-earthquake scenarios
ABSTRACT
This research aims to develop a responsive workflow that can generate 3D city models. In particular, with reference to the principles of City Information Modeling and thanks to the potential of VPLs, GIS and H-BIM approaches are combined for the prevention and post-earthquake management in minor urban historical centers.
Federico Mario La Russa, Giulia Genovese
Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Architettura, Università degli Studi di Catania